Having a Security Posture
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations must prioritize their cyber security efforts. Neglecting proper security measures can leave your organization vulnerable to data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive approach to cyber security. In this article, we will delve into the different phases of such an approach and highlight their importance in protecting your organization’s valuable assets.
Risk Assessment and Analysis
The first step in any effective cybersecurity strategy is conducting a comprehensive risk assessment. Identify and evaluate the assets, systems, and data that require protection. Assess potential vulnerabilities and threats, considering both internal and external factors. Prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. Take into account compliance requirements and industry best practices to ensure a holistic approach to risk management.
Security Policy Development
Developing a clear and comprehensive security policy is essential to provide guidance for your organization’s cybersecurity efforts. Align the policy with your organization’s goals and objectives, ensuring it covers all relevant areas. Establish guidelines and procedures for handling security incidents, user access management, data classification, and security awareness training. Involve key stakeholders, including executives, IT personnel, legal, and HR, to ensure policy buy-in and adherence.
Security Awareness & Training
Employees play a critical role in maintaining a secure environment. Educate them about the importance of cybersecurity and their responsibilities in protecting organizational assets. Conduct regular training sessions covering topics such as password hygiene, phishing awareness, social engineering, and safe browsing practices. Ensure employees understand security policies and procedures and provide resources for reporting suspicious activities. Foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness throughout the organization.
Access Management and User Controls
Implement strong authentication measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforce password policies that promote strong, unique passwords. Establish user access controls based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring users only have access to the systems and data necessary for their roles. Regularly review and update user access rights, especially during employee role changes or departures, to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Incident Response Planning
Develop an incident response plan (IRP) to effectively handle cybersecurity incidents. Define clear steps and responsibilities for incident response team members. Establish communication channels and escalation procedures for reporting and responding to incidents promptly. Conduct tabletop exercises periodically to test and refine the effectiveness of the IRP. This preparation ensures a coordinated and efficient response to minimize the impact of cyber incidents.
Security Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic and identify potential threats. Implement security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to collect and analyze log data for detecting suspicious activities. Continuously monitor system logs, network traffic, and user behavior for anomalies or indicators of compromise. Establish incident alerting mechanisms to promptly notify the appropriate personnel when potential security incidents are detected.
Vulnerability Management
Regularly scan and assess your organization’s infrastructure and applications for vulnerabilities. Establish a process for prioritizing and addressing identified vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact. Implement effective patch management procedures to ensure systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches. Monitor and track the progress of remediation efforts to ensure vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers.
Continuous Improvement and Evaluation
Protecting an organization is an ongoing effort that requires continuous evaluation and improvement. Conduct periodic audits and assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of security controls and processes. Stay updated on emerging cyber threats, trends, and regulatory changes to adapt your security measures accordingly. Learn from security incidents and industry developments to enhance your cybersecurity practices. Foster a culture of continuous improvement and accountability across the organization.
Conclusion
Preparing for cyber threats requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. Organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity preparedness by having a plan. Identifying risks, developing robust policies, training employees, managing access, planning incident response, monitoring for threats, managing vulnerabilities, and continuously improving security measures will help safeguard valuable assets, systems, and data. Prioritizing cybersecurity is an investment that pays dividends in protecting against cyber threats and maintaining a resilient and secure environment.
There are several cybersecurity frameworks that organizations can use to develop a plan for addressing cyber threats. These frameworks provide guidelines, best practices, and standards to help organizations manage their cybersecurity risks effectively. I’d like to just breifly touch on a few of these:
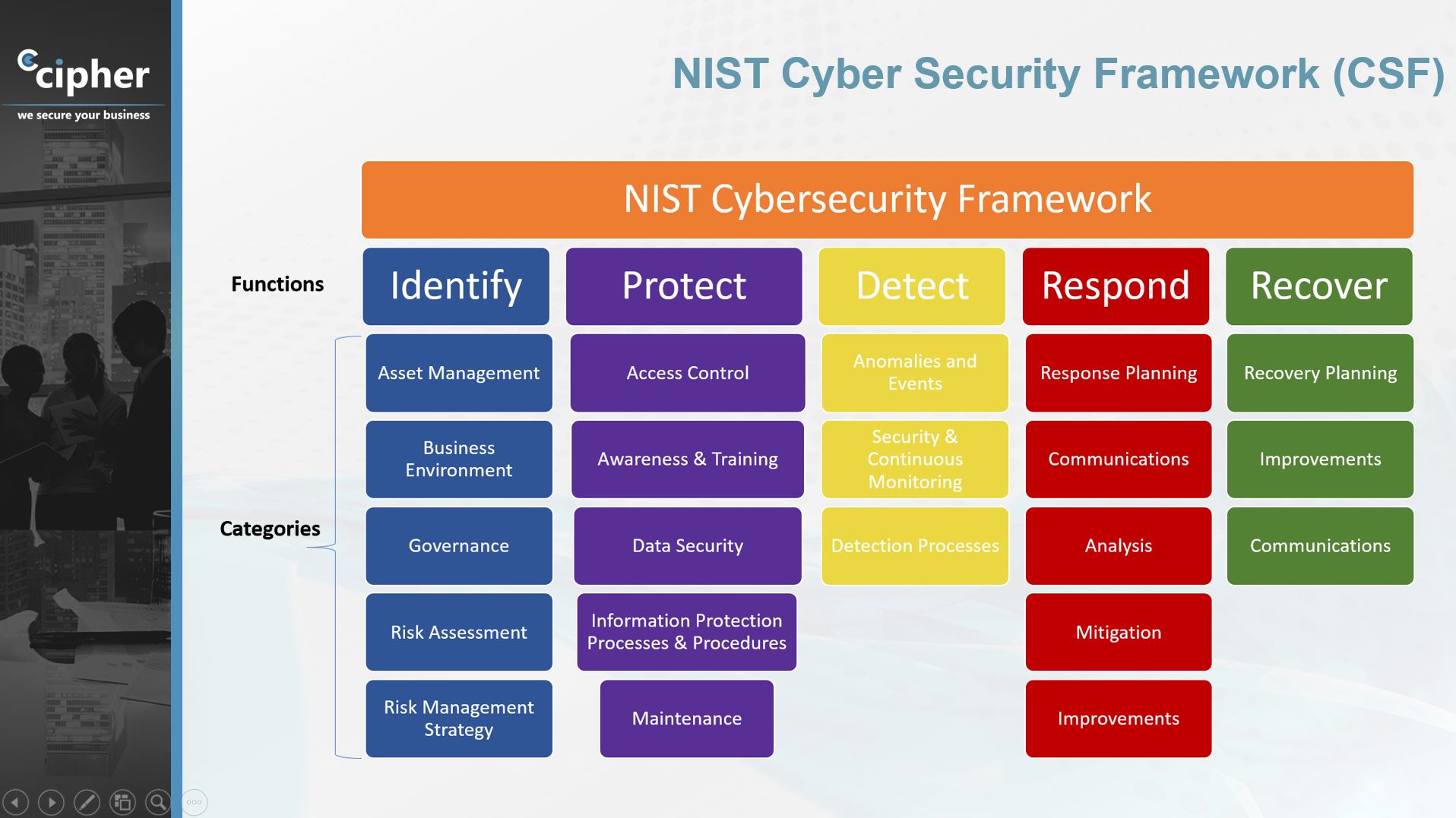
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the CSF provides a comprehensive approach to managing and reducing cybersecurity risks. It consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
ISO 27001: This is an international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach for managing sensitive information and addresses security risks in a structured manner.
CIS Controls: The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls is a set of best practices designed to help organizations safeguard their systems and data. The controls provide a prioritized framework for mitigating the most common cyber threats.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): COBIT is a framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) for IT governance and management. It focuses on aligning IT activities with business objectives and includes guidance on managing cybersecurity risks.
HITRUST Common Security Framework: The HITRUST Common Security Framework includes risk analysis and risk management frameworks, along with operational requirements. The framework has 14 different control categories and can be applied to almost any organization, including healthcare.
MITRE ATT&CK: MITRE ATT&CK is a knowledge base that describes common tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries during cyber attacks. It can help organizations understand and prepare for potential threats.
These frameworks can be tailored to an organization’s specific needs and industry requirements. These frameworks provide guidelines, best practices, and standards to help manage cybersecurity risks effectively. The choice of framework will depend on factors such as the organization’s size, resources, industry regulations, and specific compliance requirements.
1
2
3
4
┌──(root㉿servver)-[~]
└─$ vi cyberplan.txt
- ## Get Started
-